Motherboards are an important consideration when building a PC or upgrading an older one. The motherboard sizes you use decide the aesthetics of the PC and other features it will offer.
A motherboard is a printed circuit board that acts as a connector for all the significant parts of the computer. Basically, it is a plate of fiberglass with copper on it, which provides the conductive pathways in the insulator fiberglass. This plate/board has an extensive copper wiring network with various slots and ports.
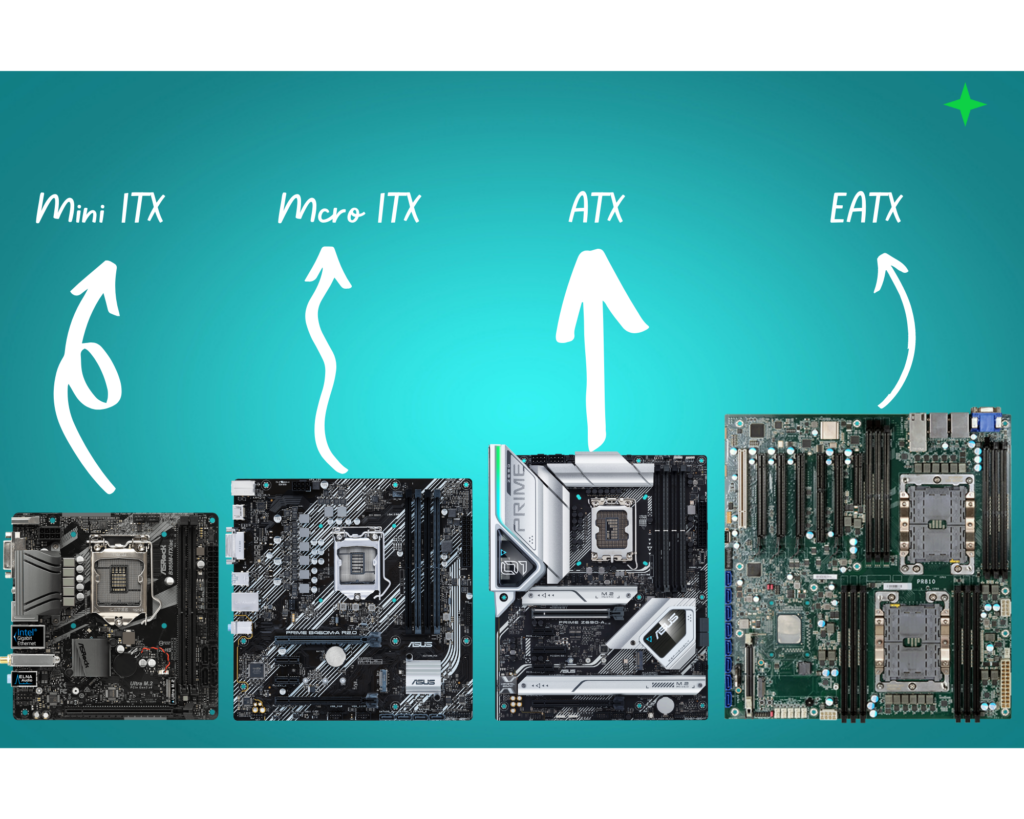
Comparison Chart For Motherboard Sizes
The number of RAM slots, M.2 ports, and other features depend upon brands. Here is a general chart comparing different sizes and form factors of motherboards.
| Feature | ATX | EATX | Micro-ATX | Mini-ITX |
| Max Size | 305 x 244 mm | 305 x 330 mm | 244 x 244 mm | 170 x 170 mm |
| RAM Slots | 4-8 | 6-8 | 4-6 | 2-4 |
| RAM Type | DDR4 | DDR4 | DDR4 | DDR4 |
| Expansion Slots | 7-13 | 12-16 | 4-7 | 1-3 |
| Graphics Card Slots | 1-3 | 1-4 | 1-2 | 1 |
| SATA ports | 6-8 | 8-12 | 4-6 | 2 |
| M.2 slots | 1-4 | 2-4 | 1-2 | 1 |
| Other features | SLI/CrossFire support, multiple PCIe x16 slots, more RAM slots | SLI/CrossFire support, multiple PCIe x16 slots, more RAM slots | PCIe x16 slot, fewer RAM slots | PCIe x16 slot, fewer RAM slots |
Major Functions Of Mother Board
Motherboards are like the backbone of a computer system. All the components of a computer are connected to this circuit board for communication and synchronization. For this, motherboards have buses that take and bring back signals from one component to another and this makes communication possible.
Amongst all the vital components of a motherboard, there is a tiny quartz crystal that plays the role of a system clock. It sends out signals at accurate time intervals so that all other components know when to work and when not to. This process is efficient in maintaining the overall synchronization of the computer system.
Another important function of the motherboard is that it holds the ROM chip for BIOS(basic input/output system). BIOS is the first program that your system accesses in order to get started. It is not possible for your system to start without a BIOS chip in the motherboard as it has all the instructions and settings that your system needs to boot. BIOS also plays a key role in managing data flow to and from the various peripherals.
Major Components Of MotherBoard
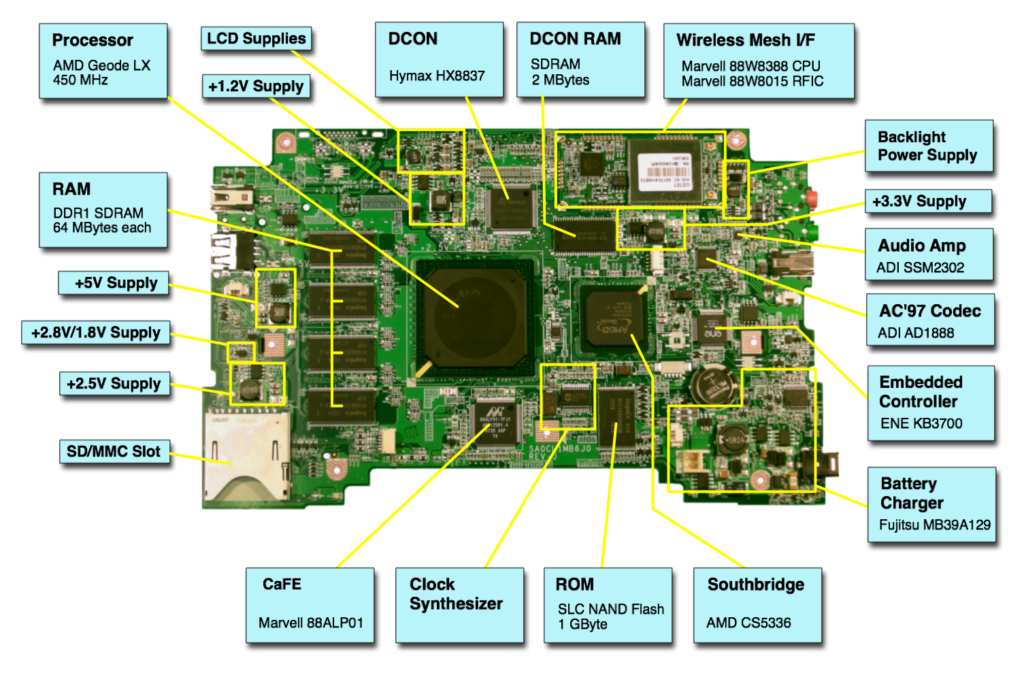
Source: Wikimedia
The motherboard has multiple components including various ports and slots, a CPU chip, and a CMOS battery.
Here is a list of some major components that play a significant role in making the motherboard functional.
- Various Ports and Slots
A motherboard has various ports for tool extension. The USB (Universal Serial Bus) port is used to connect various peripherals like the keyboard, mouse, printer, scanner, etc. to the motherboard. The catch with USB ports is that the peripherals connected through it can be inserted or removed without having to restart the computer system.
For some old devices that cannot be connected through the USB port, motherboards also have parallel ports. The motherboard also has various slots like the RAM slots which hold the RAM and connect it to the computer system. Other slots include the PCI slot (for inserting expansion cards on a computer), ISA slot (for connecting modems), AGP slot (for attaching video cards), and the power supply slot.
- CPU chip
The Central Processing unit is one of the most essential parts of a computer system and the motherboard holds accountability for having the CPU or processor embedded in it.
- CMOS battery
The complementary metal oxide semiconductor battery is used to store the BIOS program and settings, and the date and time.
Motherboard Sizes Vs Form Factors?
The form factor is a standard in computers that manufacturers follow to make sure that their parts are compatible with the motherboard. It is typically significant because it is the one that decides the overall size of the chassis. The size of the motherboard actually represents the dimensions and specifications it offers.
Generally, you may have seen motherboards with green-colored PCBs, but this is not an industry standard. You can easily find green, red, and white motherboards in the market.
What Are The Different Sizes of Motherboards?
The different sizes or form factors of Motherboards are ATX, ITX, BTX, and NLX form factors. These form factors have some extended versions. Let’s learn about them.
ATX Form Factor Motherboard
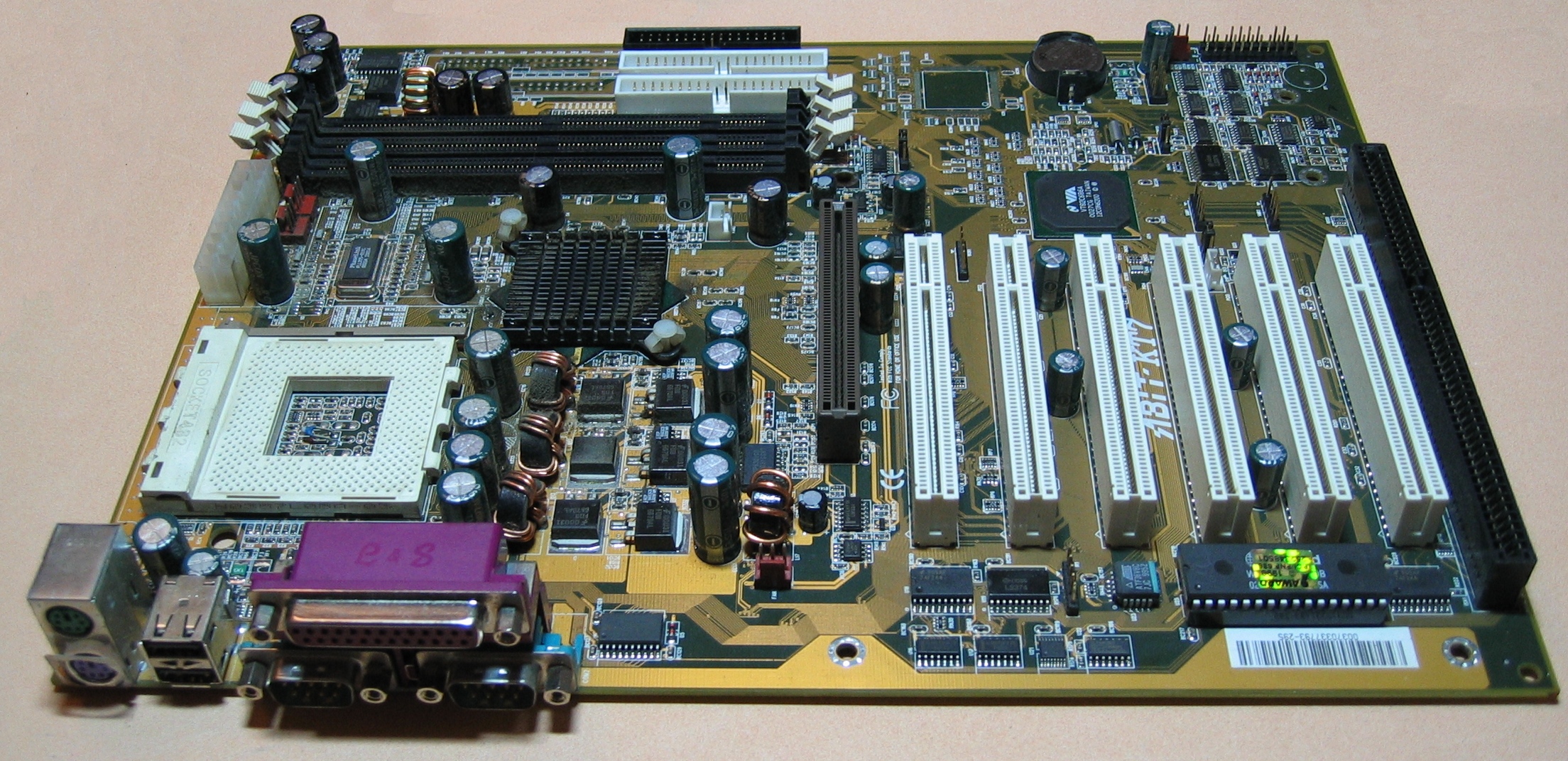
ATX Motherboard
The most common form factor used in PCs today is ATX and these are the boards that you will find most easily in the market. ATX stands for Advanced Technology Extended and it was created by Intel back in 1995. A standard ATX motherboard has dimensions of 12 x 9.6 inches OR 305 x 244 millimeters.
Its decent size allows it to have plenty of heat sinks. ATX motherboard has around 6 expansion slots and a 20-pin power connector (a modern ATX motherboard may have a 24-pin power connector). These motherboards have at least 4 memory slots as well and they can support up to 4 RAM modules. It can have as many as 7 PCI express slots.
Extended ATX (EATX) Motherboard
If you are looking for something that is larger than a regular ATX board, an extended TAX is what you will go for. It is sized 12 x 13 inches and it has more expansion slots than ATX.
It may also have more heat sinks because of the bigger size. Sometimes an EATX can sport up to 8 RAM slots along with 2 CPU sockets as well. They are difficult to find in the markets.
Micro ATX (MATX) Motherboard
This is yet another version of the ATX motherboard. As the name suggests, they are smaller than the ATX motherboards and have a square shape. Its dimension is 9.6 x 9.6 inches OR 244×244 millimeters and because it is smaller, it has fewer expansion slots than ATX- around 3 expansion slots.
They have at least 4 memory slots as well. These are cheaper as compared to ATX boards and they were designed to fit more minor computer cases.
They have a 24-pin power connector and they can support up to 4 RAM slots. They can have a maximum of 4 PCI express slots.
ITX Form Factor Motherboard
ITX Form Factor || Motherboard Sizes
Mini ITX Motherboard
These are the most miniature boards that are capable of supporting standard-sized hardware components. ITX stands for Information Technology Extended and it was developed by VIA Technologies.
The ITX form factor came out in 2001 starting with the mini ITX. This was designed keeping in mind the demand for smaller and space-saving computers. It consumes less power. So it is even easier to cool down than the bigger ATXs which also eradicates the need for heat sinks.
The mini ITX is 6.7 x 6.7 inches OR 170 x 170 millimeters and because of the very small size, it has only 1 expansion slot and only 2 memory slots. It can support only 2 RAM slots and it has only 1 PCI express slot. Most of them use a 4-pin power connector.
NOTE: The mini ITX, micro ATX, and ATX will all fit into the same computer case because of the fact that all three of these boards have their mounting holes, rear input/output panels, and expansion slots aligned.
Nano ITX Motherboard
With dimensions of 4.7 x 4.7 inches only, these are built to consume very little power. Because of size and power limitations, they are capable of supporting very limited and specific hardware components. They are used in building a PC that is small.
Pico ITX Motherboard
Pico ITX motherboards are smaller than the nano ITX boards and measure only 3.9 x 3.9 inches. They consume very little power and have very few features and expansion slots. These motherboards are basically used in the automation and IoT industry where they fit easily.
BTX Form Factor Motherboard
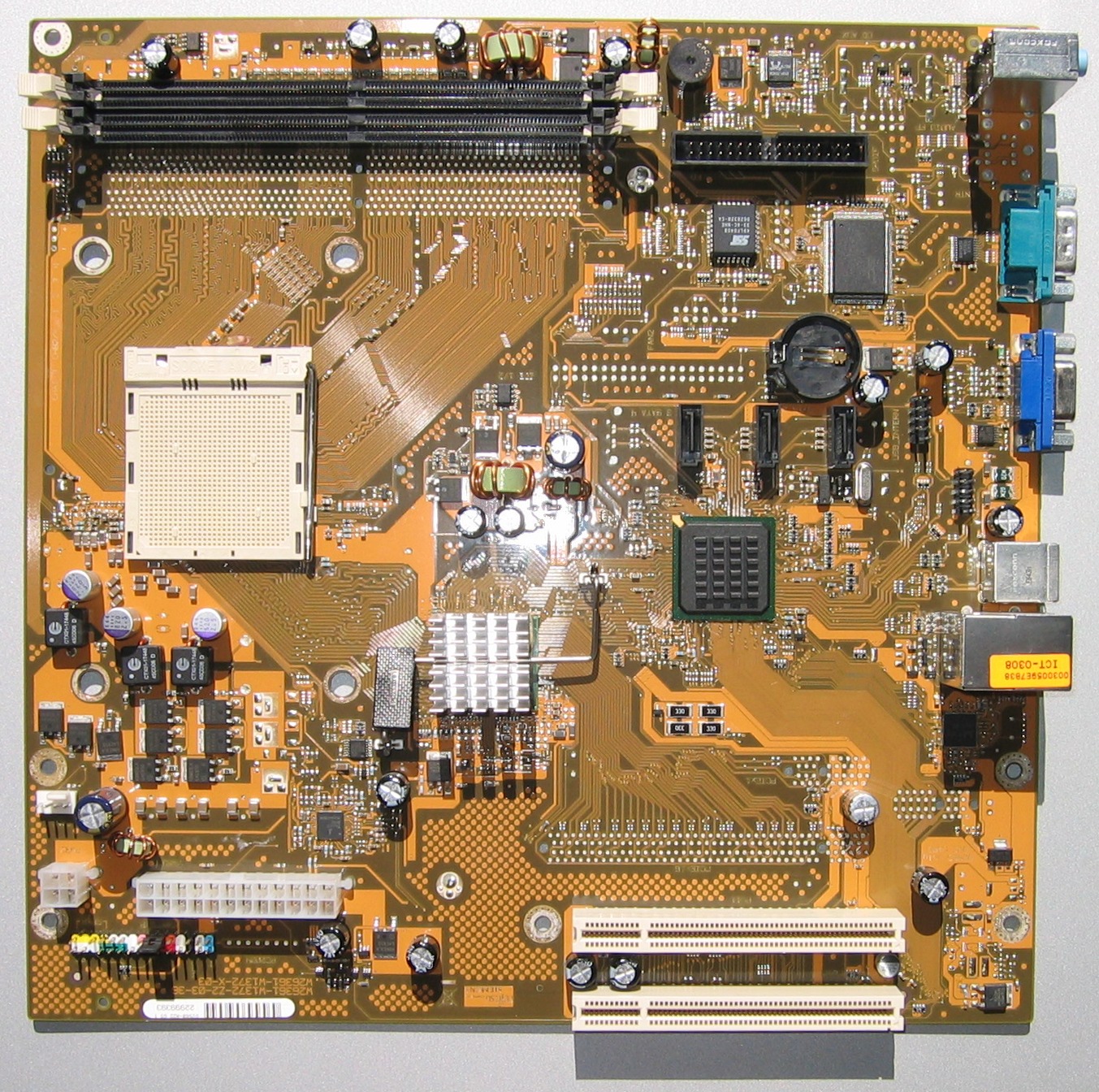
BTX motherboards were designed by Intel and it has advancements like an improved board design, with better cooling dynamics. It also has a better structural design, which is flexible enough to work on both- smaller and larger tower cases. However, BTX still stands less the ATX.
NLX Form Factor Motherboard
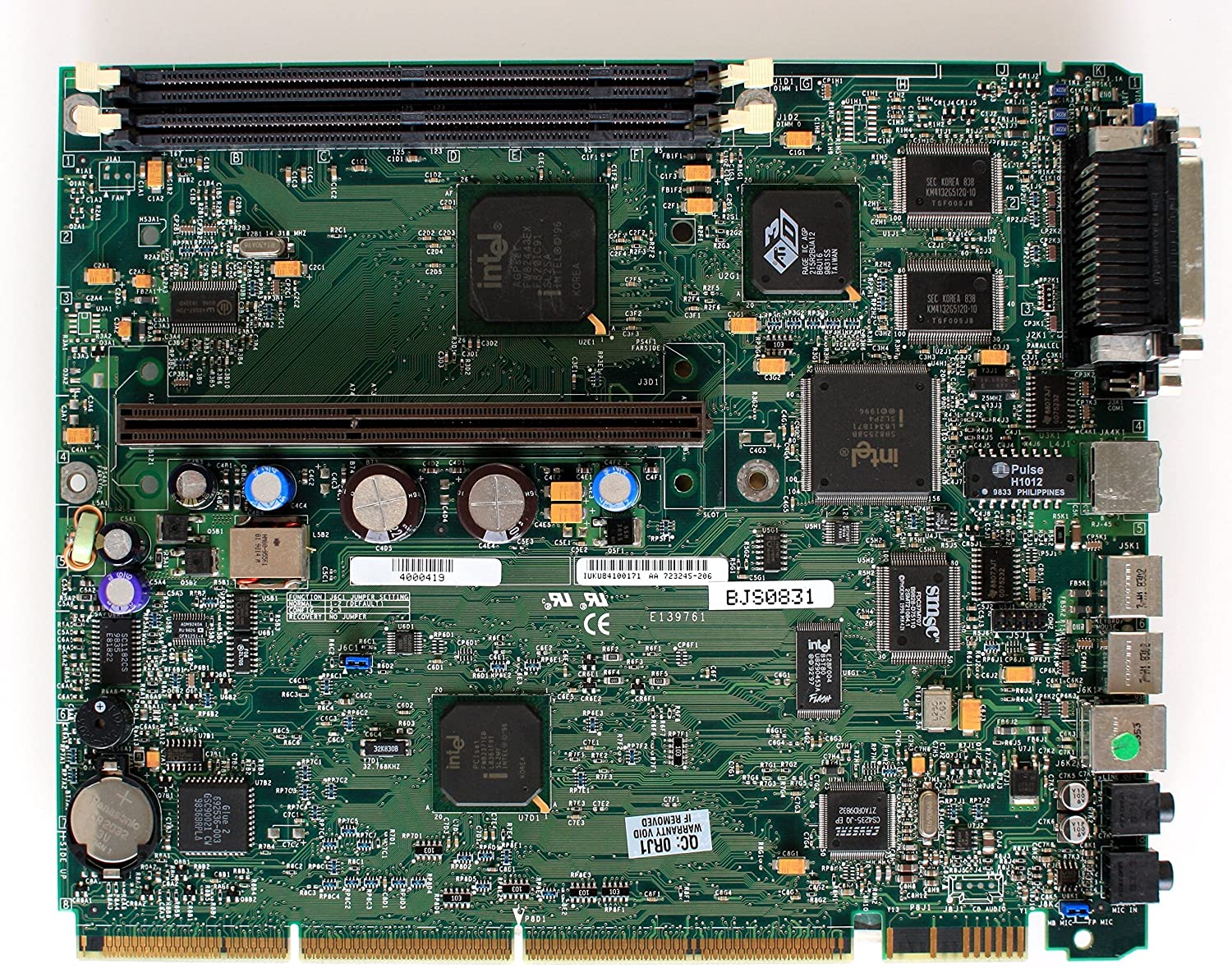
NLX is yet another form factor created by Intel for low-end, low-profile computers. The NLX board uses a riser card to plug the expansion slots in parallel to the motherboard instead of the traditional perpendicular plugging setup. These boards are typically found in slimline computer cases.
How to Check Motherboard Sizes You are Currently Using?
Knowing your motherboard type can come in handy at the time of a CPU upgrade, or when you want to purchase a processor that is compatible with your motherboard. While upgrading your memory, you will need to know your motherboard type in order to see what memory is compatible with it.
Here are a few methods of how you can easily identify the type of motherboard on your system.
Check Motherboard Type With the Command Prompt
Windows 10 PCs come with some built-in tools using which, you can find out the detailed specifications of your system, including motherboard type and model. The command prompt is one such tool.
To easily find out the motherboard type and model number on your system, open the Windows 10 command prompt. You can open the command prompt by simply typing “command prompt” in the search bar of the start menu.
Another way to launch the command prompt is through the run dialogue box, you can launch the run dialogue box with the help of shortcut keys Windows + R and type “cmd” in there and hit enter. Please note that you have to launch the command prompt simply in its default orientation and not as an administrator.
Once the command prompt is open, you have to prompt Windows Management Interface Command by giving the following instruction as it is, as the input:-
wmic baseboard get product,manufacturer,version,serialnumber
Once you enter this command and hit enter, you will see the details of your system, including motherboard details.
Check Motherboard Type With Windows System Information
Windows 10 PCs come with some built-in tools using which, you can find out the detailed specifications of your system, including motherboard type and model. The Windows system information is another such tool along with the command prompt.
To do it, first launch the run dialogue box with the help of shortcut keys Windows + R and then type msinfo32 in there. By simply doing this and then pressing enter, you will see your system’s information on the screen. Here you will find the motherboard information as well.
Note: Despite being the easiest method, it does not always provide adequate results. This method may not be compatible with some systems.
Check On The Motherboard
Sometimes we might be stuck in situations where we cannot use any software or programs to check our motherboard type. In cases where your motherboard is not installed or if your system isn’t switching ON, you can physically check for the type and model of your motherboard.
However, checking physically by disassembling is not advisable since it can mess with the original orientation and positioning of the motherboard and the various components around it, but if that’s the only option left, here’s where to check.
Different motherboards have their model number printed in different locations, depending on their form factor and type. The motherboard type and model are the largest printed text on your motherboard. Therefore, you have to look for the largest text on your motherboard where there is enough space for that large text to be printed.
You can also find the motherboard serial number printed on a sticker, at the back of your motherboard. But this is not feasible if your motherboard is already installed.
Using Third-Party Apps
There are many third-party applications and motherboard checker programs that you can install for free. These help you find out the specifications of your system, including the motherboard sizes. Two such programs and how to use them, are mentioned below.
CPU-Z
In order to get a detailed and thorough overview of a laptop’s specs, CPU-Z is a good option to use. It is free software that you can install from this website and it will give you an extensive rundown of your system’s hardware components.
Once you install and run this program, it will analyze and identify the components to give you the information. Now you just have to go to the mainboard tab of the CPU-Z program to access that information. You will find all the details of your motherboard like its model, chipset, manufacturer, etc. in the mainboard tab itself.
Belarc Advisor
Just like CPU-Z, Belarc Advisor is also a good program you can use to get a detailed and thorough overview of a laptop’s specs. You can try it for free from here. Once you run this program, it will perform a series of scans and then display the respective results in a browser tab.
You will find many details of your device here, to check the motherboard details, you will have to go to the heading that says ‘Main Circuit Board’ and click on it. You may find this option on the right side.
Are All Micro ATX Motherboards The Same Size?
Yes, all the micro-ATX motherboards of almost the same size. There can be a minor difference in width as some boards are narrow in shape. The mounting holes of all the boards are the same. There might be slight differences in the sizes but that won’t make a difference to fit in a niche PC case.
The Final Take On Different Sizes Of Motherboards
There are various types of motherboards are available in the market and are used for relevant devices. You can select a motherboard based on your requirements such as PC case size, performance you expect, color, and so on. I hope you loved reading this article on motherboards. Don’t forget to share this article with your friends.